Market Framework Model (MFM) – Backtest results / MFM validation
The Market Framework Model organizes price behavior into structural states that appear across all markets. MFM is a structural model for serious traders who want to understand how the market behaves, not a buy/sell signal tool. This page summarizes the main empirical evidence supporting those structural layers.
MFM does not project future prices or make forward targets. It is not a trading system, not a signal generator, and not a performance model. It identifies structural states that increase or decrease probability, not guaranteed outcomes.
It is a structural interpretation framework designed to reveal when markets are coherent and when they are not.
Some visualizations on this page represent the complete MFM model design, including layers that will be added to the TradingView build in upcoming releases (such as explicit Deviation overlays and HUD markers).
Structural models must be evaluated across different markets to ensure that their components behave in a consistent and observable way.
This page summarizes how MFM was examined, without presenting performance or trading results.
What this page is
This page provides a high-level overview of the backtest methodology used to evaluate the structural layers of the Market Framework Model (MFM).
It explains how the tests were performed, what the framework measures, and how MFM should be interpreted within real market environments.
The purpose is to offer transparency about the model’s design and the boundaries of its structural logic.
What this page is not
This page does not present performance results, trading signals, profit metrics or optimized configurations.
It does not show how the model would have performed in live trading.
It does not imply predictive power, guaranteed outcomes or financial advice.
All detailed structural findings, asset-by-asset observations and full backtest data are included exclusively in the Full Backtest Report that comes with the Full MFM Indicator.
Transparency statement
The sections below explain how the backtests were performed, what the model does not claim to do, and in which situations MFM becomes less reliable. The purpose is to clarify the boundaries of the framework, not to present performance results.
Backtest methodology
All assets were tested using identical MFM settings.
No asset-specific tuning, optimization or curve-fitting was applied.
This ensures that all results reflect raw structural behavior rather than engineered parameters.
The study used multi-year historical datasets for SPX, NVDA, AMZN, Gold, BTC and XRP on the 4H timeframe.
Transaction costs, slippage and execution noise were not simulated, as MFM is a structural framework, not a trading system.
The goal of the backtest is not to demonstrate performance. It is to evaluate whether the structural layers of MFM (Regime, Phase, Leadership, MPF and Deviation) behave consistently across markets with different volatility profiles.
Limitations
MFM organizes context; it does not forecast outcomes.
There are market environments where structural behavior becomes unstable:
- extreme macro events (CPI, FOMC, geopolitical shocks)
- sudden volatility expansion
- thin or fragmented liquidity
- unexpected cross-asset dislocations
In these conditions, Phase transitions may accelerate, Leadership may misalign, and MPF signals may be absent or unreliable. Such behavior is expected: structural organization decays under stress.Deviation helps highlight unstable conditions, but cannot anticipate abrupt regime shifts.
What MFM does not do
- It does not predict future prices.
- It does not identify tops or bottoms.
- It does not offer financial advice or guaranteed outcomes.
MFM provides structured context only. Users remain responsible for their own analysis and decisions.
1. Backtest Evidence – Market Framework Model (MFM)
Evidence-based structural behavior across multiple assets and volatility regimes
The Market Framework Model is built on the idea that markets do not behave randomly at the structural level.
They organize into repeatable states that can be observed across assets and timeframes.
The backtests evaluate whether these structural layers appear consistently in assets such as SPX, NVDA, Gold, BTC and XRP.
The purpose is not to demonstrate performance or predict future price.
It is to assess whether MFM reflects actual, observable market structure across different conditions.
This section provides an overview of the backtest design and the conceptual findings.
Market Framework Model (MFM)
A multi-layer structural framework for market context
| Layer | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Regime | Macrotrend bias via higher-timeframe momentum ratio |
| Phase | Internal momentum rotation cycle (MRM) |
| Leadership | Cross-asset relative strength |
| MPF | Pattern structure highlighting (pivot-anchored) |
| Deviation | Contextual anomaly and instability detection |
Protected via i-Depot (BOIP), registration no. 155670.
2. Example illustration – MFM structural layers on price data
The chart below shows how the structural layers of the Market Framework Model appear visually on real market data. It highlights the Phase fields, the higher-timeframe Regime, Leadership status, and contextual MPF markers.
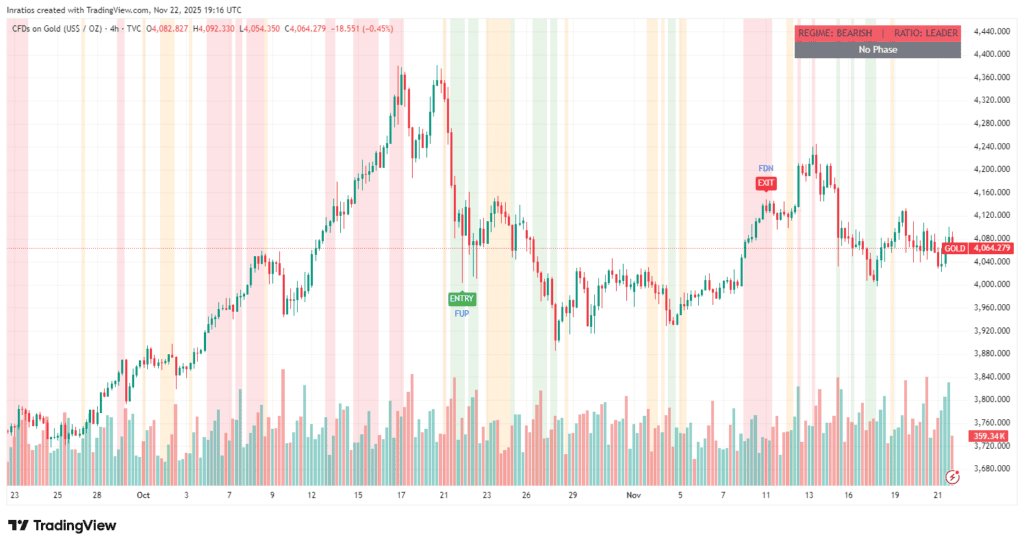
This example is illustrative only. It does not represent trading signals, performance, or expected outcomes. Its purpose is to demonstrate how MFM organizes market information into clean, interpretable structural states.
3. Why evidence matters
Structural models require more than visual appeal or intuitive logic.
To be meaningful, they must demonstrate that their internal components behave in a consistent way across different market environments.
Evidence helps confirm whether a framework reflects actual structure rather than isolated observations or curve-fitted patterns.
For MFM, the goal of validation is not to show performance or derive signals.
It is to examine whether:
- the structural layers appear in real market data,
- transitions between states are observable and repeatable, and
- the model remains stable when conditions change.
A framework that can be tested, examined and challenged is inherently stronger than one that relies on subjective interpretation.
Evidence allows users to understand why the model is designed the way it is, and where its boundaries and limitations lie.
The full backtest report provides a comprehensive view of this structural evaluation and is included with the Full MFM Indicator.
4. What the backtest summary shows
The purpose of the backtests is not to measure performance, but to evaluate whether the structural layers of MFM appear in real market data in a consistent and meaningful way.
A structural model should reveal recognizable organization across different assets, timeframes and volatility conditions — without tuning or optimization.
The backtest summary confirms that:
- the five MFM layers (Regime, Phase, Leadership, MPF and Deviation) form coherent structure in live market environments
- the transitions between structural states occur in observable, non-random ways
- each layer behaves independently, without needing asset-specific adjustments
- structural organization remains detectable across different market types
- the model maintains stability when conditions change (trending, rotating or volatile environments)
This section does not present results or performance metrics. It outlines what was examined and why structural validation matters for a context-based framework like MFM.
The complete findings are available in the Full Backtest Report included with the Full MFM Indicator.
5. Full backtest report
The complete structural evaluation, including all asset-by-asset observations, methodology details and the full backtest report, is included with the Full MFM Indicator.
This report provides the complete evidence base behind the framework and allows users to examine the structural layers of MFM in greater depth.
Disclaimer
The Market Framework Model (MFM) and all related materials are provided for educational and informational purposes only. Nothing in this publication, the indicator, or any associated charts should be interpreted as financial advice, investment recommendations, or trading signals. All examples, visualizations, and backtests are illustrative and based on historical data. They do not guarantee or imply any future performance. Financial markets involve risk, including the potential loss of capital, and users remain fully responsible for their own decisions. The author and Inratios© make no representations or warranties regarding the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of the information provided. MFM describes structural market context only and should not be used as the sole basis for trading or investment actions.
By using the MFM indicator or any related insights, you agree to these terms.
© 2025 Inratios. Market Framework Model (MFM) is protected via i-Depot (BOIP) – Ref. 155670. No financial advice.